Asynchronous operations are crucial when working with web applications. We can all agree how easy async/await has made our lives while dealing with asynchronous operations.
In this post, we are going to see how to use loops with async/await.
Before we dive into it, here are the utility functions I used for the demo
// creates a logger function to print logs with function name
function getLogger(fnName) {
return function logger(value, diffInMS) {
return console.log(
`${fnName}: Item ${value} finished waiting ${Math.round(
diffInMS / 1000
)} seconds later.`
);
};
}
// simulates an async flow, a network request for example
async function waitFor(seconds) {
// used to create the fancy waterfall
fetch("https://random-data-
api.com/api/stripe/random_stripe" + Math.random());
// the fake asynchronous task
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(resolve, seconds * 1000);
});
}
The classic For loop
const list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 , 9, 10];
export async function mainWithFor() {
const start = Date.now();
const logger = getLogger("mainWithFor");
for (const item of list) {
await waitFor(2);
const later = Date.now();
logger(item, later - start);
}
}
Runs the code sequentially, one by one. Waiting for each waitFor to finish before proceeding to the next iteration.
The image below shows a nice waterfall demonstration, look how each green section starts 2 seconds after the previous one. (don't worry about their duration, as it's a random endpoint. Only for the sake of waterfall depiction)
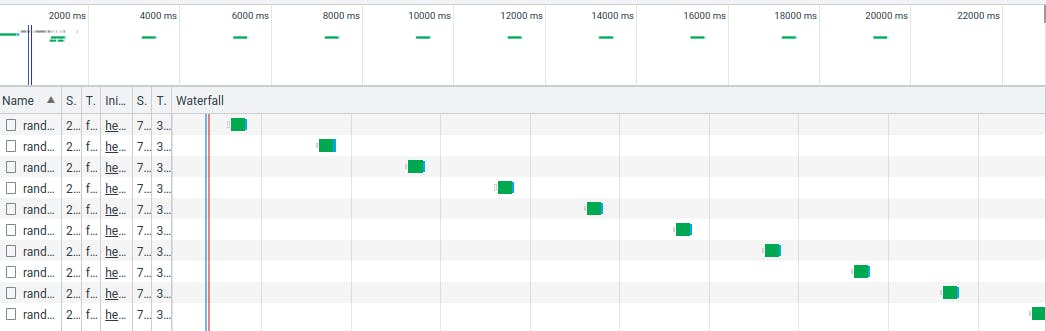
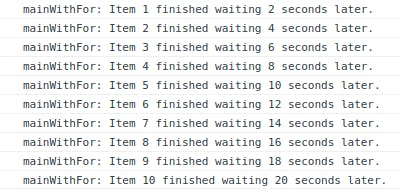
You'll also notice that the logs appear at a 2-second difference, one by one.
A good use case for this approach would be to run sequential operations, where you want the next operation to run once the former has finished.
The forEach higher-order method
export async function mainWithForEach() {
const start = Date.now();
const logger = getLogger("mainWithForEach");
list.forEach(async (item) => {
await waitFor(2);
const later = Date.now();
logger(item, later - start);
});
}
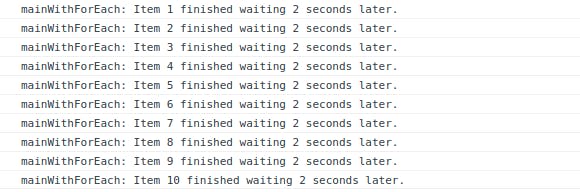
The forEach loop acts differently than the for loop, while the for loop await the iteration before moving further, the forEach loop executes all of the iterations simultaneously. So all the ten executions start at the same point and log after 2 seconds.
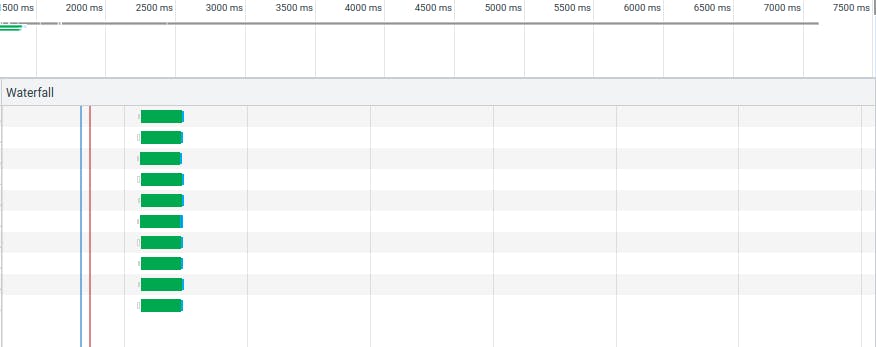
We can also observe the same using a waterfall diagram, look how they all began at the same time. (Again please ignore the duration of each execution, it's random-api).
A good use case for this approach would be to run parallel operations, where you don't care if the previous one finished or not. It's much faster compared to
forloop. But there is a caveat to this approach: if the api you're requesting has some sort of rate-limiting setup then making simultaneous requests can backfire.
The map higher-order method
export async function mainWithMap() {
const start = Date.now();
const logger = getLogger("mainWithMap");
const promises = list.map(async (item) => {
await waitFor(2);
const later = Date.now();
logger(item, later - start);
});
const finalAnswer = await Promise.all(promises)
}
The map function behaves exactly the same as forEach in terms of async operations, meaning all of the callbacks start at the same time and log exactly after 2 seconds.
On top of this, the .map returns an array of promises, (one promise per execution, in the same order).
Later we can do a await Promise.all(promises) to get the final answer array from it.
It should be noted that the Promise.all will reject completely if even a single one of the promises from the input array rejects.
mapshould be used at places where you would need to return some data based on each async operation. If that's not the case, sticking withforEachwouldn't be a bad choice.
Here is the link to codesandbox, in case you want to try this out yourself.
I have also created a YouTube video giving hands-on explanation to this post, {% youtube Ce1ywrKeStI %}
I hope you enjoyed reading this article as much as I enjoyed writing it!
For more such posts, please follow me on Twitter
Until next time

